
You start the process by pulling air into the machine. Fans or blowers move the air from the surrounding environment into the system. The speed and amount of air you draw in matter a lot for making water efficiently.
An airflow velocity of about 2 meters per second works best for these machines.Tip: If you want the best results, make sure the air intake is not blocked and the fans are working well. Good airflow means more water.
Before the air reaches the cooling or condensation stage, you need to clean it. Air often contains dust, pollen, and even tiny pollutants from cars or factories. If you do not filter these out, they can end up in your water.
HEPA filters work best for this job. They can remove 99.97% of particles as small as 0.3 microns. Some machines use electrostatic fibers with HEPA filters to catch even more particles. However, you must pay attention to maintenance, as clogged filters can slow down the process and increase energy use. Other filter types, like ionic purifiers or ozone generators, are less effective and can even make the air less safe.
Air quality affects both the safety and the amount of water you get.Note: Some chemicals in the air, like ammonia, can still get into the water even after filtration. You should always check and maintain your system to ensure safe drinking water.
After the air passes through the filters, you need to cool it down to collect water. Most air to water making machine use two main methods: refrigeration-based cooling and desiccant-based absorption.
Refrigeration-based systems work by cooling the air below its dew point. When you lower the temperature, water vapor in the air turns into liquid water. This process is similar to how water droplets form on a cold glass on a hot day. These systems use compressors and coils, much like a refrigerator or air conditioner. You get the best results when the relative humidity is above 30-35%. If the humidity drops below this level, the machine will not work well, and water production can stop completely. For example, some machines stop making water when the humidity falls to around 37%. You will see the highest water output when the humidity is closer to 60% or higher.
Desiccant-based systems use special materials that absorb water from the air. These materials, called desiccants, can pull moisture even when the air feels dry. Silica gel, lithium chloride, and new materials like metal-organic frameworks (MOFs) work well for this job. After the desiccant collects water, you heat it up to release the water as vapor, then cool it to turn it into liquid. This method uses less electricity and can work in places where the air is very dry, such as deserts. Some advanced desiccant systems can collect water when the humidity is as low as 20%. You can use solar power or other renewable energy to heat the desiccant, making the process more energy-efficient.
Tip: If you live in a dry area, a desiccant-based air to water generator may work better for you than a traditional cooling system.
Once the air cools or the desiccant releases moisture, the next step is to collect the water. In refrigeration-based systems, water forms on cold surfaces called condensers. The machine then channels this water into a storage tank. In desiccant-based systems, the released vapor cools and condenses into water, which also flows into a collection tank.
The amount of water you can collect depends on the machine and the weather. For example, a typical residential air to machine that makes water from air like the GENNY can produce up to 30 liters of drinking water per day under standard conditions. This is enough for a small family’s daily needs.
You may wonder how much water you get for the energy you use. The table below shows how much water different refrigeration-based machines can make for each kilowatt-hour (kWh) of electricity:
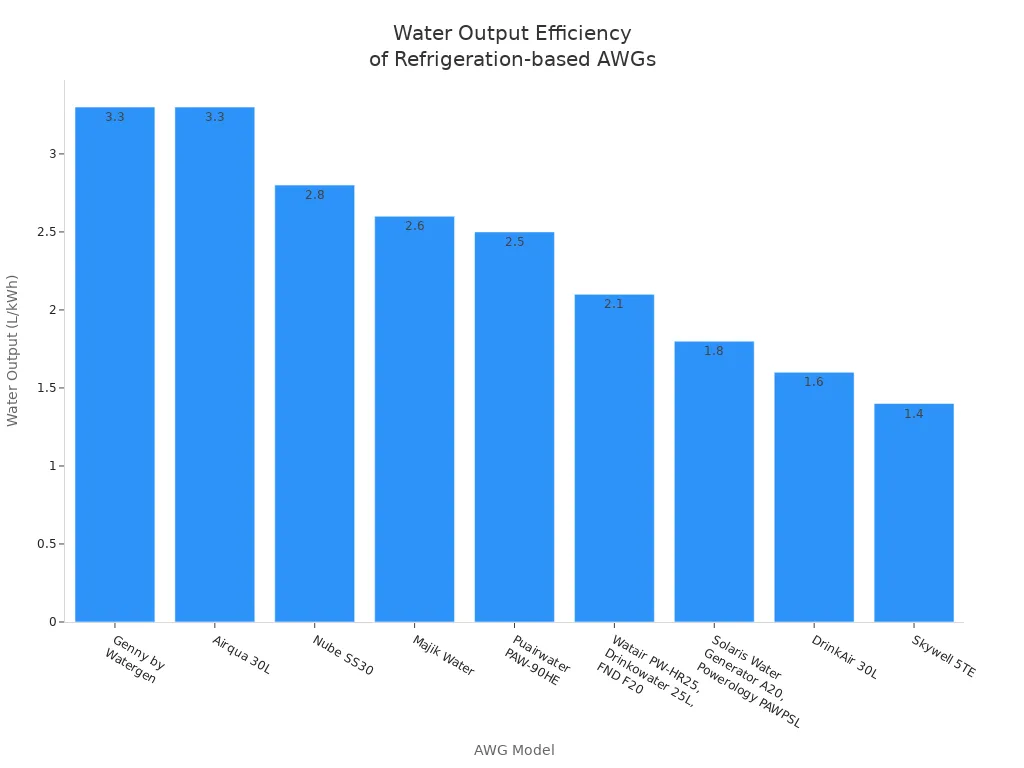
Desiccant-based systems do not use electricity in the same way. They often use solar heat or gas to release water from the desiccant. These systems can make between 1.5 and 3.3 liters of water per square meter of solar collector area each day. Their water output depends on sunlight and the type of desiccant used.
New designs help machines collect more water from the air. Some engineers copy nature by making surfaces that act like desert plants or insects. These surfaces use tiny structures and special coatings to catch water drops and move them quickly into the tank. For example, some machines use three-dimensional surfaces with hydrophobic nanowires and hydrophilic microchannels. This design keeps water from flooding the surface and helps move droplets away fast. Tests show that these surfaces can transfer heat over twice as well as regular surfaces, which means you get more water with less energy.
Note: These new surfaces and coatings make atmospheric water generator manufacturers more efficient, especially in places where water is hard to find.
After collecting water from the air, you need to make sure it is safe to drink. The purification process removes harmful substances and kills germs. This step is very important because water from the air can still contain many contaminants.
When you use an air to water generator, the water may contain several types of contaminants before purification. These can include:
SedimentsTo remove these, most machines use a multi-stage filtration system. Each stage targets different impurities. You can see how these filters work in the table below:
|
Filtration Stage |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Air Filtration |
Multi-layer air filters remove dust and dirt from incoming air |
|
Water Filtration |
Multi-layer water filtration including a three-stage ultrafiltration filter element (CP+UF+C) |
|
Disinfection |
LED UV sterilization ensures microbial safety |
Some systems add even more protection. For example, you may find a sub-micron barrier filter that removes particles smaller than 2.5 microns. Water then passes through a cascade of certified water filters. These steps help remove color, odor, dissolved salts, and particles as small as 5 microns. Some machines also use an ozone filter to destroy microorganisms and provide extra purification.
Tip: Always check if your air to water generator meets the IAPMO/ASSE Standard 1090-2020. This standard ensures the water is safe, free from harmful chemicals, and meets strict performance requirements.
After filtration, the next step is disinfection. Most air to water generators use ultraviolet (UV) light for this purpose. UV treatment uses UVC light, usually at a wavelength of 254 nanometers, to damage the DNA and RNA of bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens. This process stops them from reproducing and makes the water safe to drink.
UV systems work very quickly and do not use chemicals. They do not change the taste or smell of the water. You get clean water without any added substances. For UV treatment to work best, the water should be clear. That is why pre-filtration is important. If the water has too many particles, the UV light cannot reach all the germs.
You will find UV treatment in many water systems, including city water supplies. It is a proven method for killing a wide range of microorganisms. The effectiveness depends on water clarity, UV intensity, and how well you maintain the system. When you combine UV treatment with multi-stage filtration, you get water that is both clean and safe.
Note: Certified air to water generators must use both filtration and disinfection methods, like UV light, to meet safety standards. This ensures you always get water that is safe to drink.
When you collect water from the air, it often lacks the minerals found in natural spring water. To make the water healthier and better tasting, you need to add essential minerals. Most systems use a remineralization filter for this step. As the water passes through, the filter infuses it with minerals that your body needs.
Calcite and magnesium are the most common minerals added.This step does more than just improve taste. It also ensures the water supports your health by providing minerals your body uses every day.
Tip: If your water tastes flat or bland, check if your system’s mineral filter needs replacing.
After mineralization, you must keep the water clean and safe until you drink it. Storage tanks play a big role in this. Most systems use fully sealed tanks made from food-grade, contamination-resistant materials. This design keeps out dust, insects, and other pollutants.
To prevent microbial growth, you should:
Store water in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area.Some advanced systems use sensors to recirculate water through filters, keeping it fresh and safe. These features help maintain the water’s quality and taste, so you always have clean water ready to drink.

When you look inside an air to water generator, you find several important parts that work together to make clean water. Each part has a special job:
Air intake system: Fans and filters pull in air from the room and remove dust or dirt.Tip: If you want your air to water generator to last longer, keep these parts clean and check them often.
You might wonder how much energy these machines use. Most air to water generators need between 0.05 and 0.22 kilowatt-hours (kWh) of electricity to make one liter of water. The table below shows some examples:
To keep your machine working well, you need to follow a regular maintenance schedule:
Every week, run the machine without making water and check for leaks or alarms.
Each month, clear away any debris and check the oil and battery.
Twice a year, have a technician inspect the belts, filters, and electrical parts.
Once a year, replace filters, check the coolant, and have a full inspection.
Note: Always keep a log of your maintenance. This helps you spot problems early and keeps your water safe.
A well-maintained air to water generator can last many years and give you safe water every day.
You can see how an air to water generator turns air into safe drinking water by following these steps:
Absorb moisture from air using a desiccant or cooling system.
Heat or cool to release and condense water vapor.
Store water in a sealed, clean tank.
This process uses renewable energy and works even in remote or disaster-prone areas. Many models run off solar power and provide water where you need it most.
You can get between 10 and 30 liters of water per day from a home unit. The exact amount depends on the humidity and temperature in your area. Higher humidity means more water.
Yes, the water is safe if you maintain your machine and replace filters as needed. The system uses filtration, UV light, and mineralization to make sure the water meets drinking standards.
You can use special desiccant-based models in dry areas. These machines work even when humidity is low. Standard models may not produce much water if the air is too dry.
You should check filters every month and replace them as needed. Clean the storage tank regularly. Schedule a full inspection once a year to keep your machine running well.
Most machines use about 0.05 to 0.22 kilowatt-hours of electricity for each liter of water. You can lower energy costs by choosing a model that matches your climate and needs.
 online service
online service sale@accairwater.com
sale@accairwater.com +86 18559227773
+86 18559227773